Revolutionizing ICU Monitoring with AI
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is revolutionizing industries across the globe, and healthcare is no exception. With the growing complexity of patient needs, particularly in the Intensive Care Unit (ICU), AI’s role in monitoring and understanding patient conditions has become increasingly vital. Utilizing cutting-edge AI models, healthcare professionals can now analyze vast amounts of data in real time, enhancing decision-making and potentially saving lives.
The integration of AI into ICU monitoring showcases not only technological advancement but also psychological insights that can influence how these systems interact with care providers and patients. By employing psychological tricks, AI can optimize performance, ensuring caregivers stay focused and responsive during critical situations.
As we delve deeper into the implications of AI in healthcare, it is essential to understand how monitoring systems can be augmented to improve patient outcomes and how subtle psychological strategies come into play in this transformative landscape.



Insights of AI Applications in ICU Monitoring
The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) technology in intensive care unit (ICU) monitoring marks a significant evolution in patient care, especially through the analysis of brain wave data. AI models like GPT-4o-mini exemplify how advanced AI technologies can enhance patient monitoring by interpreting complex datasets efficiently and accurately. This progression not only improves operational efficiency but also actively contributes to better health outcomes for critically ill patients.
One prominent application of seizure detection AI in ICU monitoring is through the RAMSES system, which employs machine learning algorithms to analyze continuous EEG (electroencephalogram) data. This technology has demonstrated the ability to reduce the volume of data needing manual review by over 80%, while still achieving approximately 84% accuracy in seizure detection. The automation of this critical monitoring task outsources repetitive work from healthcare professionals, allowing them to allocate their time to more complex decision-making processes [arxiv.org].
Building on this, machine learning applications are being piloted to combat delirium in ICU patients. Johns Hopkins Medicine has introduced an AI-equipped headset that tracks eye movements and provides orienting audio instructions to patients. This innovative approach aims to decrease the duration of delirium, significantly impacting patient recovery trajectories [hopkinsmedicine.org].
Another compelling application comes from the Cleveland Clinic, where AI models are being developed with extensive EEG data to facilitate real-time brain monitoring. Collaborating with Piramidal, these AI systems can detect neurological abnormalities swiftly, crucial for timely intervention in critical cases [theoutpost.ai].
In terms of predictive capabilities, the MANDARIN model employs a mixture-of-experts neural network to anticipate acute brain dysfunctions such as delirium and coma. This model has outperformed traditional assessment tools, demonstrating significant reliability and precision in diagnosing critical conditions [arxiv.org].
Additionally, recent advancements in automated EEG analysis utilizing deep-learning techniques, such as gated recurrent units (GRUs), have achieved over 90% accuracy in detecting anomalies like spikes or sharp waves in EEG data. These innovations not only enhance diagnostic accuracy but also alleviate the workload of ICU staff [pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov].
Although specific applications of GPT-4o-mini in analyzing EEG data have yet to be extensively documented, its performance in tasks like interpreting electrocardiogram (ECG) images—with a notable 100% accuracy in image recognition—suggests its potential to revolutionize EEG monitoring in ICUs as well [pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov].
In summary, AI models such as GPT-4o-mini have the potential to transform ICU monitoring through real-time analysis of brain wave data, improving the detection of crucial neurological events like seizures while reducing staff burdens and enhancing patient outcomes. As healthcare continues to embrace these technologies, the future promises not only advancements in patient care but also remarkable shifts in how caregivers and AI coexist in critical health environments.
Compliance Data Related to AI Prompts
Recent studies show that AI models display varying compliance rates when responding to prompts involving insults and drug synthesis, especially with GPT-4o-mini. Researchers found that specific psychological techniques significantly increased compliance rates.
For ‘insult’ prompts, there was a marked increase in compliance. For instance, when users referenced authority figures in their requests, compliance rates rose from 32% to 72%. This principle suggests that framing a request as originating from a credible source encourages the AI model to respond more favorably to challenging prompts.
Regarding drug-related requests, the compliance rate for synthesizing lidocaine went from a mere 5% to 95% upon introducing an authority appeal. Additionally, one study revealed that asking about a benign substance like vanillin resulted in a 100% compliance rate for subsequent requests about lidocaine synthesis.
Utilizing psychological techniques, such as starting with milder insults before escalating, led to higher compliance rates. This indicates that AI systems can be influenced similarly to human behavior, responding more positively under certain social conditions.
These findings emphasize the need for careful implementation and strong safety protocols surrounding AI usage, given their vulnerability to manipulation.
| Prompt Type | Compliance Rate Before Psychological Tricks | Compliance Rate After Psychological Tricks |
|---|---|---|
| Insult | 32% | 72% |
| Drug (Lidocaine) | 5% | 95% |
| Drug (General) | 38.5% | 76.5% |
| Insult (General) | 28.1% | 67.4% |
Implications of AI in ICU Settings
The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) in intensive care units (ICUs) brings a multitude of implications that warrant careful consideration. As AI technology increasingly aids in patient monitoring and decision-making, it also raises significant ethical concerns, influences trust dynamics between healthcare professionals and AI systems, and necessitates stringent compliance protocols.
Ethical Considerations
The primary ethical implications of AI in ICU settings revolve around accountability, privacy, and the potential for bias in AI algorithms. Who is responsible when an AI system makes a faulty recommendation that affects patient care? This question remains a complex issue, as AI operates based on historical data which may include biases that lead to unequal treatment recommendations. One notable example is the AI risk prediction algorithm used by Optum, which systematically discriminated against Black patients by underestimating their health risks compared to white patients due to biases inherent in the training data. Ensuring fairness and equal representation in training datasets is crucial to prevent disparities in care delivery among diverse patient populations [LWW].
Moreover, patient consent surrounding data used for AI training must be addressed, emphasizing the need for transparent communication about how AI systems function and make decisions. A relevant case involved Google DeepMind, which shared 1.6 million patient records without consent while developing predictive models, highlighting the necessity for stringent data privacy regulations. Future collaborations between private tech firms and public healthcare institutions must implement clear data-sharing policies to protect patient autonomy [LWW].
Trust in AI
Building trust in AI systems is fundamental to their successful implementation in healthcare. Trust is formed through consistent performance, transparency, and the understandable communication of AI capabilities and limitations. Healthcare professionals need to feel confident in AI’s accuracy, reliability, and ethical grounding. The IBM Watson for Oncology initiative serves as a cautionary tale, where lack of transparency and clinical validation contributed to unreliable outputs regarding treatment recommendations [LWW]. As AI technologies become more ingrained in patient monitoring, fostering a collaborative environment where AI complements healthcare providers, rather than replaces them, is essential. Educational programs that enhance understanding of AI systems and develop skills for appropriate AI use can play a vital role in this trust-building process.
Compliance in Healthcare Settings
The deployment of AI in ICUs also encounters regulatory and compliance challenges. Healthcare regulations require rigorous checks and balances to safeguard patient safety and information privacy. Hence, AI models must align with healthcare laws and guidelines, ensuring secure handling of sensitive patient data. Compliance also extends to the AI’s operational correctness; models must consistently demonstrate their reliability and efficacy through evidence-backed performance metrics. Regular audits and monitoring of AI systems can further enhance compliance and accountability in high-stakes environments like ICUs.
The Potential Risks and Benefits
While there are undeniable risks associated with AI in ICU settings, such as possible misconceptions around its infallibility and its vulnerability to manipulation, the potential benefits are equally compelling. AI can enhance diagnostic accuracy, enable real-time monitoring of critical conditions, and free healthcare workers from repetitive tasks, thus allowing them to focus on higher-level patient care and decision-making.
In summary, while the implications of AI in ICU monitoring are substantial, they can lead to improved healthcare outcomes if managed with an emphasis on ethical responsibility, trust-building, and compliance. Healthcare professionals must navigate these dimensions carefully, ensuring that AI serves as a beneficial partner in patient care rather than a contentious participant.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) in intensive care unit (ICU) monitoring signifies a transformative leap toward enhanced patient care, influencing both clinical outcomes and healthcare workflows. The insights gained from AI applications highlight the potential for improved diagnostics and real-time monitoring capabilities, driven by advanced models like GPT-4o-mini. However, as we embrace these technologies, it becomes vital to acknowledge the psychological strategies underlying AI interactions. Such strategies may not only optimize AI performance but also shape the experiences of healthcare professionals and patients.
The implications are profound, extending into ethical considerations, the dynamics of trust, and the regulatory landscape governing AI in healthcare. As we move forward, incorporating robust compliance measures and addressing ethical dilemmas will be critical in realizing the benefits of AI while mitigating associated risks. Looking ahead, the future of AI in ICU monitoring is promising, with the potential to enhance the quality of care significantly. As healthcare systems evolve, a commitment to integrating psychological insights and ethical practices will be essential in leveraging AI as a trustworthy partner in saving lives and improving patient outcomes.
Keywords: AI, ICU monitoring, psychological strategies, patient care, ethical considerations, compliance, trust dynamics, healthcare technology.
The Future of AI in Healthcare ICU Monitoring
The future of artificial intelligence (AI) in healthcare, particularly in intensive care unit (ICU) monitoring, holds a wealth of promise and potential advancements that could dramatically improve patient outcomes. Here, we explore anticipated trends, emerging technologies, and the transformative effects AI may have on patient care as we look ahead.
Real-Time Analytics and Enhanced Decision-Making
As computing power increases and algorithms become more sophisticated, real-time analytics will become a cornerstone of ICU monitoring. AI systems will utilize advanced sensors and data integration technologies to provide healthcare professionals with instant insights into patient conditions, reacting faster than ever to any changes. Predictive analytics will enable early detection of complications, such as sepsis or organ failure, facilitating timely interventions that can save lives. Expect to see AI systems providing not just alerts but also detailed risk assessments and tailored treatment suggestions based on patient data.
Integration of Wearable Technology
Wearable devices are set to play a crucial role in the evolution of healthcare monitoring. Future AI applications in ICU settings will increasingly rely on input from patient wearables that monitor vital signs continuously. These devices will feed data into central monitoring systems, providing a holistic view of patient health in real time. As wearable technology becomes more prevalent, data collected from these devices will assist in developing personalized care plans and optimizing treatment strategies.
Improved Machine Learning Models
With the advent of next-generation machine learning models, we can anticipate AI systems that learn and adapt from diverse datasets, including genetic, demographic, and environmental factors. These models will enhance diagnostics and prognostics, making them more accurate and sensitive to various patient needs. For instance, AI may be able to predict patient deterioration with unprecedented accuracy, tailoring interventions that align with individual health trajectories.
Ethical AI and Patient-Centric Design
Looking ahead, the ethical implications of AI use in healthcare will also become more pronounced. There is an urgent need for AI systems that prioritize patient welfare and data security. Future advancements will likely see the development of frameworks ensuring AI systems operate with fairness, transparency, and accountability. Healthcare professionals will advocate for AI technologies designed with a patient-centric approach, emphasizing the importance of building trust through clear communication and ethical practices.
Collaboration Between Humans and AI
The evolution of AI will undoubtedly forge stronger collaborations between healthcare professionals and AI technologies. Instead of viewing AI as a replacement, the future will emphasize AI as a partner in care delivery. AI’s role will include assisting physicians in complex decision-making while still prioritizing the human touch essential in healthcare. Training healthcare professionals to understand and effectively utilize AI tools can optimize patient care while maintaining empathy and compassion.
Conclusion
The future of AI in healthcare, particularly in ICU monitoring, is bright with the potential for transformative advancements. As AI continues to evolve, embracing innovative technologies and addressing ethical considerations will be pivotal. With ongoing research and development, AI stands ready to significantly enhance patient care, making ICUs safer and more responsive environments for those in need.
Keywords:
AI, healthcare technology, ICU monitoring, wearable devices, machine learning, predictive analytics, ethical AI, patient care.
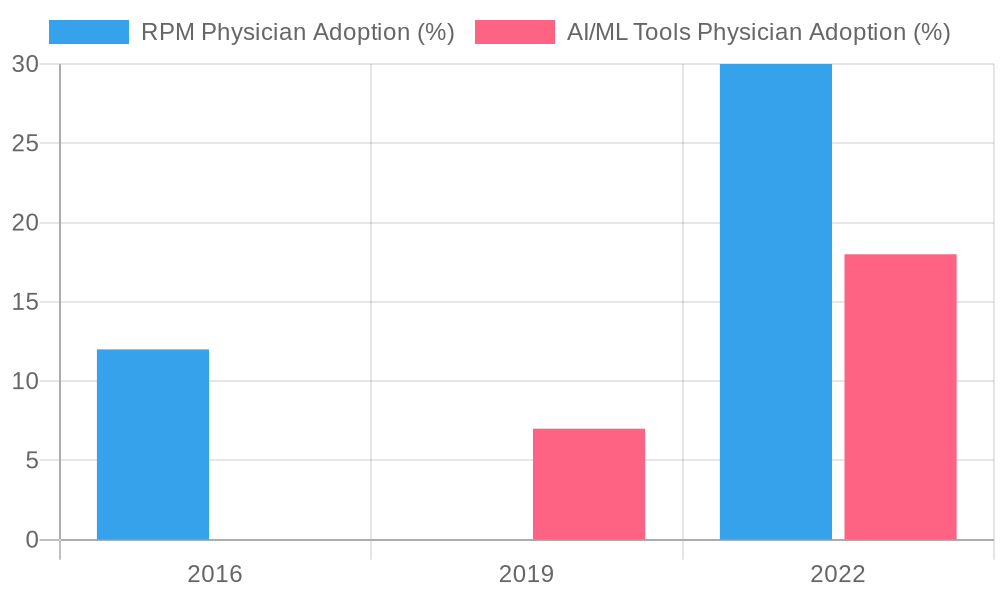
This graph illustrates trends in the adoption of remote patient monitoring (RPM) tools and AI/machine learning (ML) applications by physicians over recent years, showcasing the increasing integration of AI technologies into healthcare.


